

Fun and crazy days here at Nutanix. I’ve busy been fielding a lot of calls around our new offering, CPS Standard on Nutanix. Now if you don’t know what CPS is, it stands for Cloud Platform System.
Category Archives: Windows Azure Pack
Understanding Windows Azure Pack – Reconfigure portal names, ports and deploy certificates – Part 6

Happy New Year Everyone!!! I know Azure Stack is just around the corner, but I still get lots of questions around configuring WAP and portals. So to follow-up my Windows Azure Pack (WAP) series, I am going to talk about reconfiguring server names and ports as well as assigning trusted certificates to my WAP Portals.
Understanding Windows Azure Pack – How to guide with Express Edition on Nutanix – Windows Azure Pack Install – Part 5
To continue Windows Azure Pack series here is my next topic: Installing and Configuring Windows Azure Pack
If you missed other parts of the series, check links below:
Part 1 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack
Part 2 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack – Deployment Scenarios
Part 3 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack – How to guide with Express Edition on Nutanix – Environment Prep
Part 4 – Deploying Service Provider Framework on Nutanix
Again to reiterate from my previous blog posts and set some context, Windows Azure Pack (WAP) includes the following capabilities: Continue reading
Understanding Windows Azure Pack – How to guide with Express Edition on Nutanix – Deploying Service Provider Foundation – Part 4
To continue the Windows Azure Pack series, here is my next topic: Installing and Configuring Service Provider Foundation
If you missed other parts of the series, check links below:
Part 1 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack
Part 2 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack – Deployment Scenarios
Part 3 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack – How to guide with Express Edition on Nutanix – Environment Requirements
There are 2 main steps to deploying WAP (Windows Azure Pack) on Nutanix:
- Deploying SPF (Service Provider Foundation) – This blog post
- Deploying Windows Azure Pack (coming soon)
Service Provider Foundation
SPF is provided with System Center 2012 – Orchestrator, a component of System Center 2012 R2. SPF exposes an extensible OData web service that interacts with System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM). This enables service providers and hosters to design and implement multi-tenant self-service portals that integrate IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) capabilities available on System Center 2012 R2. The following picture shows how System Center w/SPF interacts with WAP to provide VM Cloud Services (see TechNet article for more info):
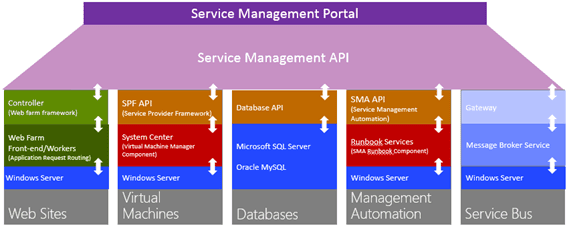 As with every installation, SPF requires additional software, features and server roles. Setup wizard checks prerequisites and reports about their status. Unfortunately, there is no “button” to install all of requirements automatically. I’ve wrote a script to automate this process (see below). Please note: Don’t try to install SPF on the SCVMM Server. It’s not supported.
As with every installation, SPF requires additional software, features and server roles. Setup wizard checks prerequisites and reports about their status. Unfortunately, there is no “button” to install all of requirements automatically. I’ve wrote a script to automate this process (see below). Please note: Don’t try to install SPF on the SCVMM Server. It’s not supported.
Requirements:
- SQL Server 2012 SP1 or higher instance (Already Deployed)
- OS – Windows Server 2012 R2 VM (Already Deployed)
- 2 CPU Cores
- 4 Gigs of RAM
- 100 Gig OS Drive
- Feature – Management OData Internet Information Services (IIS) Extension
- Feature – NET Framework 4.5 features, WCF Services, and HTTP Activation.
- Web Server (IIS) server. Include the following services:
Basic Authentication
Windows Authentication
Application Deployment ASP.NET 4.5
Application Development ISAPI Extensions
Application Deployment ISAPI Filters
IIS Management Scripts and Tools Role Service - Downloads:
WCF Data Services 5.0 for OData V3
ASP.NET MVC 4 - Virtual Machine Manager 2012 R2 Console
- Certificates: self-signed (wizard creates one automatically) or obtained SSL-certificate (recommended for production)
This script will install all requirements except SCVMM console (please note that SCVMM console has to be installed manually):
#IIS + Process activation model
Install-WindowsFeature Web-Asp-Net45,Web-Scripting-Tools,Web-Basic-Auth,Web-Windows-Auth,NET-WCF-Services45,Web-ISAPI-Ext,Web-ISAPI-Filter,Web-Scripting-Tools,WAS-Process-Model,WAS-Config-APIs,ManagementOdata
#Download and install WcfDataServices and AspNetMVC4
New-Item C:SPFRequirements -ItemType Directory
Invoke-WebRequest http://download.microsoft.com/download/8/F/9/8F93DBBD-896B-4760-AC81-646F61363A6D/WcfDataServices.exe -OutFile C:SPFRequirementswcfdatasvc.exe
Invoke-WebRequest http://download.microsoft.com/download/2/F/6/2F63CCD8-9288-4CC8-B58C-81D109F8F5A3/AspNetMVC4Setup.exe -OutFile C:SPFRequirementsaspnetmvc.exe
Set-Location C:SPFRequirements
.aspnetmvc.exe /quiet
Wait-Process aspnetmvc
.wcfdatasvc.exe /quiet
Wait-Process wcfdatasvc
Write-Host “All prerequisites are installed. Insert your SCVMM 2012 R2 DVD and install SCVMM Console manually. Then your environment will be ready for SPF installation“
Required user accounts
- spfadmnsvc – SPF Admin Web Service
- spfprovsvc – SPF Provisioning Web Service
- spfusagesvc – SPF Provisioning Web Service
And the following domain group
- SPF_Admins – Group for SPF Administrators – Add all your WAP admins to this gorup
This admin group should be added to the local Administrators group on the SPF server.
Certificates
The Service Provider Foundation provides an extensible OData web service. Communications to this web service can and should be encrypted by SSL. SSL requires certificates. The Service Provider Foundation allows for self-singed certificates (for testing purposes) and certificates issued by a standalone Certificate Authority, an enterprise Certificate Authority or a public Certificate Authority. The Service Provider Foundation install defaults to self-signed (wizard creates one automatically) or you can obtain a certificate from a Public CA for production.
Installation
The Service Provider Foundation setup is on the System Center Orchestrator R2 media.
When installing, login to the SPF server as a user that has DBO/SA rights to the SQL 2012 instance that will be hosting SPF databases.






Define application pool credentials (spfadminsvc) and SPF_Admin Group that will have an access to SPF services and click Next. It’s best practices to create new domain accounts for every SPF services instead of using Network Service account.

Provider Web Service properties , click Next

Usage Web Service configuration, click Next

Windows updates + CEIP – yes (Microsoft needs your feedback 🙂 ), click Next

Click Install

Setup is complete!

Update SPF with the latest rollup (https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/3021802) or use Windows Update.
Please note, the latest roll-up causing an issue in IIS and breaks SPF Web from working. I ran into this during my lab deployment. Check out this blog post on “System Center 2012 R2 : Update Rollup 4 breaks the SPF website” that fixes the issue.
This completes the SPF install. In a future blog post, we will be integrating SPF with WAP and SCVMM.
Additional links:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj642895.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn266007.aspx
Next up in my series, Installing the Windows Azure Pack on Nutanix
Until next time, Rob….
Understanding Windows Azure Pack – How to guide with Express Edition on Nutanix – Environment Prep – Part 3
To continue the Windows Azure Pack series, here is my next topic: Windows Azure Pack – Environment Prep
If you missed parts 1 or 2 in the series, check links below:
Part 1 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack
Part 2 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack – Deployment Scenarios
Environment Prep
In the first blog posting in this series we examined the capabilities and benefits of deploying WAP (Windows Azure Pack) in enterprise datacenters by first looking at Windows Azure, Microsoft’s public cloud offering.
In the second blog posting we looked at some of the terminology associated with WAP and we summarized two kinds of deployment scenarios on Nutanix: Express and Distributed architecture
Moving on…”Cloud” is the buzz word in all aspects of our computing life today, and more and more companies want to be able to offer the benefits of a “Cloud” environment to their on premises users. And by now, we should all know the Public Cloud (i.e. Azure, Amazon, etc.) might not suit everyone and is definitely not suited for all situations….That is where Nutanix and WAP standout;
Giving your the ability to have a predictable, scalable , highly available, high performing IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) hybrid datacenter
This series is meant to be a guide to building your own WAP test lab on Nutanix and also provide you guidance for building out a production Nutanix WAP environment.
WAP Test Environment Requirements
Just to see functionally, you could deploy it the requirements on one host with Nutanix CE (Community Edition), but building this WAP environment on a Nutanix cluster will give you real world results.
In this series, we will be building 2 VM’s for the WAP test environment. The VM’s consist of SPF (Service Provider Foundation) Server and Windows Azure Pack Server.
In my test lab, I am using a 4 Node Nutanix NX3050 Cluster with Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V. This blog post assumes you have an Active Directory Domain and SCVMM (System Center Virtual Machine Manager) 2012 R2 up and running. It also assumes you have an empty SQL 2012 SP1 server built for hosting SPF, WAP and Tenant SQL Databases.
In this Post:
- Installing Hyper-V on Nutanix
- Hyper-V Networking Overview
- SCVMM Server / Fabric Prep
- Self-Service Users (tenants) storage of VMs in the SCVMM Library
WAP Pre-requisites:
- Virtual Machine Manager is installed and configured and:
- Member of the Active Directory domain.
- One or more SCVMM Clouds created in SCVMM (see below video)
- One or more VM Networks created in SCVMM (see below video)
- Service Provider Foundation
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- 4 Gigs of RAM
- 2 CPU Cores
- Database Storage
- Member of the Active Directory domain
- Windows Azure Pack Server
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- 4 Gigs of RAM
- 2 CPU cores
- 20 Gigs Data Storage
- Database Storage
- Member of the Active Directory domain
- SQL Server is installed and running
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- SP1 or Above
- 16 Gigs of RAM
- 2 CPU Cores
- 100 Gigs Data and Log Drive
- With Mixed or SQL Authentication enabled
- Member of the Active Directory domain
If you need help building a SCVMM 2012 R2 Server, check out my blog post on Installing SCVMM 2012 R2 on Nutanix (coming soon).
If you need help building a SQL 2012 Server, check out my blog post on Install SQL 2012 on Nutanix (coming soon)
If you need help deploying Hyper-V to a Nutanix cluster and joining the cluster to an Active Directory Domain, see my buddy Chris Brown’s Blog Video on Installing Hyper-V on Nutanix. This also covers adding it to SCVMM 2012 R2. He also has a great Hyper-VSCVMM Networking Overview. Another great NutanixMicrosoft resource.
Installing Hyper-V on Nutanix
Hyper-V Networking Overview
SCVMM Server / Fabric Prep
Account requirements
The Active Directory security account groups below are recommended as best practices when deploying WAP with SCVMM. Active Directory Security were created and mapped in SCVMM as Delegated Administrations. See screenshots below.
Self-Service Users (tenants) storage of VMs in the SCVMM Library
You will also need to create a library share, or create a folder in a library share that will serve as the storage location for tenants. Also, understanding that self-service users must have the Store and Re-Deploy permission to store their virtual machines in important. In my test lab, I created a Nutanix container (SMB Share) with compression attributes and presented it to SCVMM.
IMPORTANT RULES FOR LIBRARY SHARES
- The library share location that you designate for stored virtual machines must be different from the shares that you designate as read-only resource locations for the private cloud.
- The path or part of the path must be unique when compared to the user role data path that is specified for a self-service user role
- You could also create entirely separate library shares with containers on Nutanix,like I did above
- Understand that you will configure the stored virtual machine path and read-only library shares when you run the Create Cloud Wizard as shown video below.
- The self-service user role data path is specified when you create a self-service user role or modify the properties of a self-service user role.
- Make sure that one or more library shares exists that you can assign as the read-only library shares for self-service users to use.
- The library shares that you designate as read-only resource locations for the private cloud must be unique when compared to the library share or shares that are used for stored virtual machines and for the user role data path that is specified for a self service user role.
Creating Tenant Storage and Private Cloud in SCVMM 2012 R2 on Nutanix
In high level, best practices is to have each tenant how their own separate storage containers as shown in below diagram. This will allow you to advertise available capacity, security boundaries, and apply attributes, like deduplication or compression on a per container basis and then tie it up to storage classifications in SCVMM.
Next is to create storage for you tenants. In Prism, create a new container with the name of your tenant, set an advertised capacity and add any storage attributes, like deduplication or compression depending on the type of workloads being hosted. See the below a video I produced with my buddy @Mike TME at Nutanix of the process:

If you have any questions about the prep, please comment below.
Yea, now we can finally deploy the WAP. Now the fun part starts…..
Next up in my series, Installing the Windows Azure Pack environment on Nutanix – Deploying SPF (Service Provider Foundation)
Understanding Windows Azure Pack – Deployment Scenario’s on Nutanix – Part 2
To continue the Windows Azure Pack series, here is my next topic: Deployment Scenario’s on Nutanix
If you missed part 1 – see link below
Part 1 – Understanding Windows Azure Pack
Windows Azure Pack – Deployment Scenario’s
Terminology
Ok, Let’s start with some terminology used when talking about WAP(Windows Azure Pack). Here are two key terms you need to know:
- Administrator – Someone who deploys, configures and manages WAP and makes cloud services available to tenants.
- Tenant – Someone who subscribes to and uses cloud services made available through WAP.
When WAP is deployed by a hoster (service provider) the administrator refers to IT staff at the hoster while the tenants are the customers to which the hoster is selling cloud services. And when WAP is deployed in an enterprise datacenter, the administrator will be your own IT department; the tenants in this case will be the other departments, divisions, or business units within your organization that want to take advantage of the cloud services your IT department is offering.
 Admin Portal
Admin Portal
 User Signin Portal
User Signin Portal
 User Main Portal
User Main Portal
Required components
WAP currently includes eight components. Two of these components are portals:
- Management Portal for Administrators – A web-based portal that lets administrators configure and manage user accounts, resource clouds, tenant offers, and so on.
- Management Portal for Tenants – A web-based self-service portal that lets tenants provision, monitor and manage the following cloud services: Web Sites, Virtual Machines, and Service Bus.
The self-service capabilities of the Management Portal for Tenants enables tenants to deploy and manage the cloud services they need when they need them without having to go through the slow procurement processes of the traditional approach to enterprise IT.
Authentication is another key feature of WAP to ensure that only properly authenticated administrators have access to the Management Portal for Administrators and only properly authenticated users have access to the Management Portal for Tenants. By default, the Management Portal for Administrators uses Windows authentication (Kerberos or NTLM) but you can optionally use Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) for authentication purposes. The Management Portal for Tenants on the other hand uses the ASP.NET Membership Provider for authentication purposes. WAP includes two authentication sites, an Admin Authentication Site and a Tenant Authentication Site, for these purposes.
WAP also includes components that provide the following application programming interfaces (APIs):
- Windows Azure Pack Admin API – Enables administration tasks to be performed using the Management Portal for Administrators and Windows PowerShell.
- Windows Azure Pack Tenant API – Enables tenant-specific tasks to be performed using the Management Portal for Tenants and Windows PowerShell.
- Windows Azure Pack Tenant Public API – Provides additional tenant-specific functionality primarily for hosting provider environments.
All of the above components are required in any WAP deployment.
Optional components
The following components of WAP may be deployed in order to offer additional forms of cloud services and other resources to tenants:
- Web Sites – Provides you with a managed web environment you can use to create new websites or migrate your existing business website into the cloud.
- Virtual Machines – Provides you with a general-purpose computing environment that lets you create, deploy, and manage virtual machines running in the Windows Azure cloud.
- Service Bus – Allows you to keep your apps connected across your private cloud environment and the Windows Azure public cloud.
- Automation and Extensibility – Allows you to automate and integrate custom services into your services framework using runbooks.
- SQL and MySQL – Allows you to provision Microsoft SQL and MySQL databases for tenants to use.
Windows Azure Pack – Deployment Scenario’s
There are two basic deployment scenarios for WAP:
- Express architecture – Recommended for proof of concept testing only.
- Distributed architecture – Recommended for production environments.
In addition, the distributed architecture can be implemented in various ways depending on the scale and degree of availability needed. Let’s briefly examine each of these scenarios.
Express architecture
In an express deployment of Windows Azure Pack, you install all of the required components on a single server and any optional components needed on one or more additional servers. This is the deployment I will be doing in the next part of the series. Specifically, the following required components must all be installed on your first server:
- Windows Azure Pack Admin API
- Windows Azure Pack Tenant API
- Windows Azure Pack Tenant Public API
- Admin Authentication Site
- Tenant Authentication Site
- Management Portal for Administrators
- Management Portal for Tenants
In addition, your first server must host the SQL Management Database used by the required components. This means you must install a required version of Microsoft SQL Server on the first server.
Distributed architecture
In a distributed deployment of WAP, you spread out the required components across multiple servers. There are many ways you can do this, but the following recommendations should generally be adhered to in order to ensure optional performance and supportability for your deployment:
- Install a management portal and its corresponding authentication site on the same server. For example, install the Management Portal for Administrators and the Admin Authentication Site on the same server.
- If you will be providing cloud services to tenants over the public Internet, install the following components on the same public-facing server:
- Management Portal for Tenants
- Tenant Authentication Site
- Windows Azure Pack Tenant Public API
- If Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) is to be used for authentication purposes, install it on a separate identity server.
- If Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is to be used for authentication purposes, install it on a separate identity server along with an ADFS
- For greater scalability and high availability in large deployments, install the SQL Management Database on a separate failover cluster. In addition, use failover clustering for your public-facing servers and for the servers hosting your other required components.
- For even higher scalability, install each required component on a separate failover cluster and the SQL Management Database on another failover cluster. In other words, use eight failover clusters to deploy the seven required components plus the SQL Management Database. Check out Nutanix Best Practices guide for deploying SQL
In the next blog post in this series, we will begin our walk-through of installing and configuring WAP. I will focus primarily on the express deployment scenario in this series along with two types of cloud services: Virtual Machines and SQL Databases…………..Let’s build a cloud……
Until next time, Rob…
Understanding Windows Azure Pack – Part 1
With Azure Stack coming early next year….Windows Azure Pack is still of great value currently for service providers to organizations wanted to provide IaaS (Infrastructure as a service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service). I get asked all the time “What is Azure Pack”, “How do you deploy and what do I get started? etc…This blog series will give you the fundamental rundown on Windows Azure Pack and how it compares to Windows Azure Public Cloud…Deployment Scenarios on Nutanix and a how to deploy step-by-step Azure Pack express edition on Nutanix. So sit back and enjoy the show…
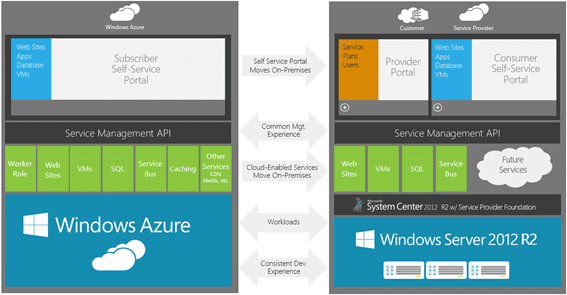
What is Windows Azure?
To understand what Windows Azure Pack is, you first need to be familiar with Windows Azure, Microsoft’s public cloud platform. To understand what Windows Azure is all about, check out the Azure website, but here are some key points of Windows Azure:
- Windows Azure for service hosting and management, low-level scalable storage, computation and networking
- Microsoft SQL Services for a wide range of database services and reporting
- Microsoft .NET Services which are service-based implementations of familiar .NET Framework concepts such as workflow and access control
- Live Services for a consistent way for users to store, share and synchronize documents, photos, files and information across their PCs, phones, PC applications and Web sites
- Microsoft SharePoint Services and Microsoft Dynamics CRM Services for business content, collaboration and rapid solution development in the cloud.
As a cloud platform from Microsoft that provides a wide range of different services, Windows Azure lets you build, deploy, and manage solutions for almost any purpose you can imagine. In other words, Windows Azure is a world of unlimited possibilities. Whether you’re a large enterprise spanning several continents that needs to run server workloads, or a small business that wants a website that has a global presence, Windows Azure can provide a platform for building applications that can leverage the cloud to meet the needs of your business…
So now, Let’s look at the definition that Microsoft uses for describing Windows Azure:
Windows Azure is an open and flexible cloud platform that enables you to quickly build, deploy, and manage applications across a global network of Microsoft-managed datacenters. You can build applications using any language, tool, or framework. And you can integrate your public cloud applications with your existing IT environment.
This definition tells us that Windows Azure is a cloud platform, which means you can use it for running your business applications, services, and workloads in the cloud. But it also includes some key words that tell us even more:
- Open – Windows Azure provides a set of cloud services that allow you to build and deploy cloud-based applications using almost any programming language, framework, or tool.
- Flexible – Windows Azure provides a wide range of cloud services that can let you do everything from hosting your company’s website to running big SQL databases in the cloud. It also includes different features that can help deliver high performance and low latency for cloud-based applications.
- Microsoft-managed – Windows Azure services are currently hosted in several datacenters spread across the United States, Europe, and Asia. These datacenters are managed by Microsoft and provide expert global support on a 24x7x365 basis.
- Compatible – Cloud applications running on Windows Azure can easily be integrated with on-premises IT environments that utilize the Microsoft Windows Server platform.
Windows Azure provides businesses with four basic categories of cloud-based services:
- Compute services
- Network services
- Data services
- App services
At the core of the Windows Azure platform is its ability to execute applications running in the cloud. Windows Azure currently provides four different models for doing this: Web Sites, Virtual Machines, Cloud Services, and Mobile Services. Together these four approaches comprise the compute services portion of the Windows Azure platform, and they can either be used separately or combined together to build more complex solutions that can meet specific business needs.
Now, let’s go though some the main options on Windows Azure….
Windows Azure Web Sites is a scalable, secure, and flexible platform you can use for building web applications that run your business, extend the reach of your brand, and draw in new customers. It has an easy-to-use self-service portal with a gallery of the world’s most popular web solutions including .DotNetNuke, CakePHP, DasBlog, WordPress, and many others. Or you can simply create a new website from scratch and then install a tool like WebMatrix—a free, lightweight web development tool that supports the latest web technologies such as ASP.NET, PHP, HTML5, CSS3, and Node. You can use WebMatrix to create websites and publish applications for Windows Azure. And if you use Microsoft Visual Studio as a development environment, you can download and install a Windows Azure SDK so you can build applications that can take advantage of the scalable cloud computing resources offered by Windows Azure…
Creating a new website with Windows Azure is so easy we have to show you how to do it. Begin by logging on to the Windows Azure Management Portal at https://manage.windowsazure.com using your Microsoft Account username and password. Then select the Compute, Web App tab on the left and either click Quick Create or click the from Gallery button on the command bar as shown here:
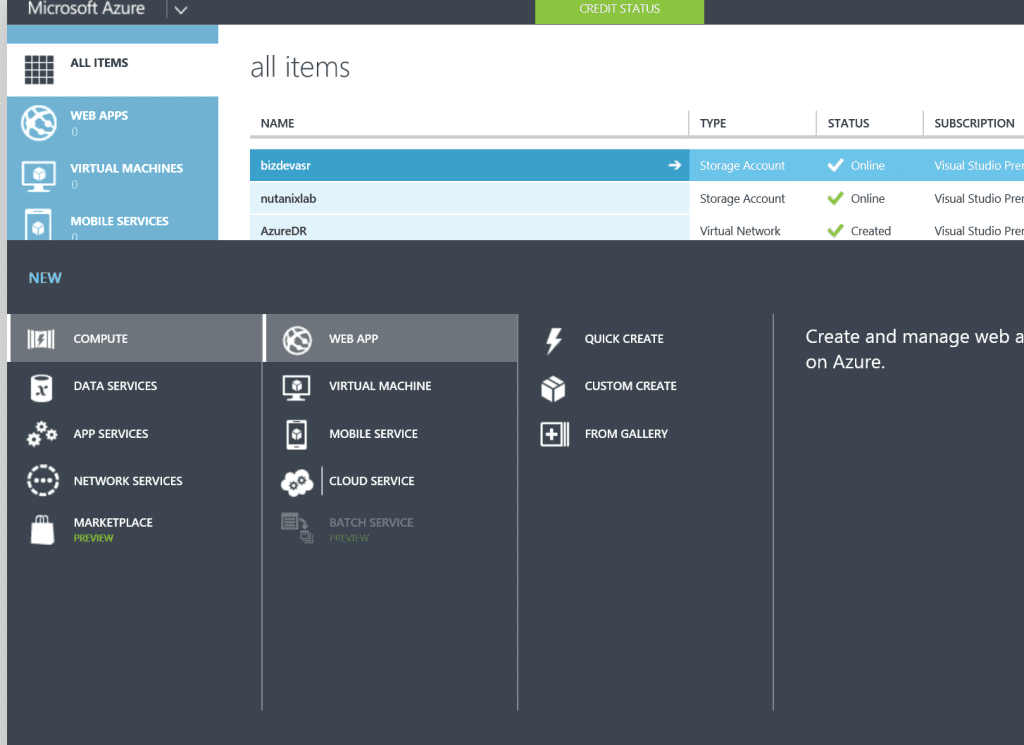 The command bar then expands, as shown in the next figure, and allows you to quickly create a new website with no additional configuration, a custom website with either a new or existing database, or a new web application based on an application framework, blog engine, template, or any other app available in the Windows Azure gallery…
The command bar then expands, as shown in the next figure, and allows you to quickly create a new website with no additional configuration, a custom website with either a new or existing database, or a new web application based on an application framework, blog engine, template, or any other app available in the Windows Azure gallery…
Windows Azure Virtual Machines is a scalable, on-demand IaaS platform you can use to quickly provision and deploy server workloads into the cloud. Once deployed, you can then configure, manage, and monitor those virtual machines, load-balance traffic between them, and connect them to other Windows Azure Cloud Services running web roles and worker roles. You can copy virtual hard disks (VHDs) from your on-premises environment into Windows Azure to use as templates for creating new virtual machines. And you can copy VHDs out of Windows Azure and run them locally in your datacenter.
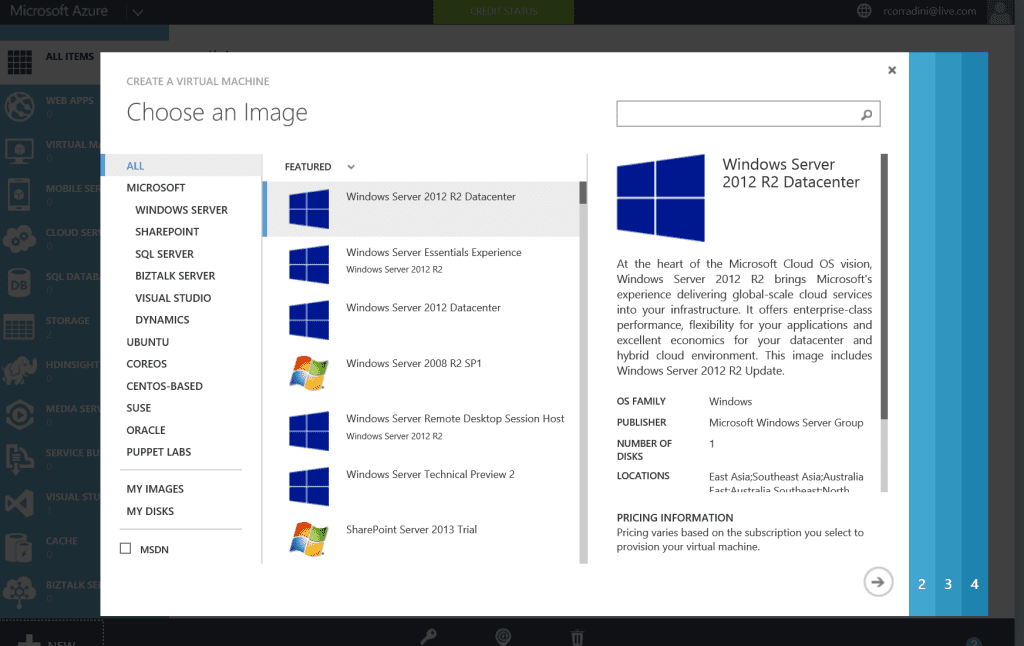
You can create new virtual machines from a standard image available in the Windows Azure gallery. Standard images are included for current versions of Windows Server and for different flavors of Linux. Standard images are also available for Microsoft SharePoint, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Dynamics and Microsoft BizTalk Server pre-installed on Windows Server. Standard images are a great way of quickly provisioning new virtual machines, but you can also use images you created on-premises to deploy new virtual machines.
Creating a new virtual machine in Windows Azure is easy. Just open the Windows Azure Management Portal and select Compute, and then Virtual Machine tab on the left. The command bar expands and displays two options for creating virtual machines: Quick Create or From Gallery.
The Quick Create option lets you create a new virtual machine which you can configure later. As shown below, all you need to specify for this option is the DNS name for your virtual machine, the image to use as a template for your virtual machine, the size of the virtual machine (number of cores and memory), a user name and password for administrative access to the virtual machine, and the region or affinity group to which the virtual machine should be assigned:
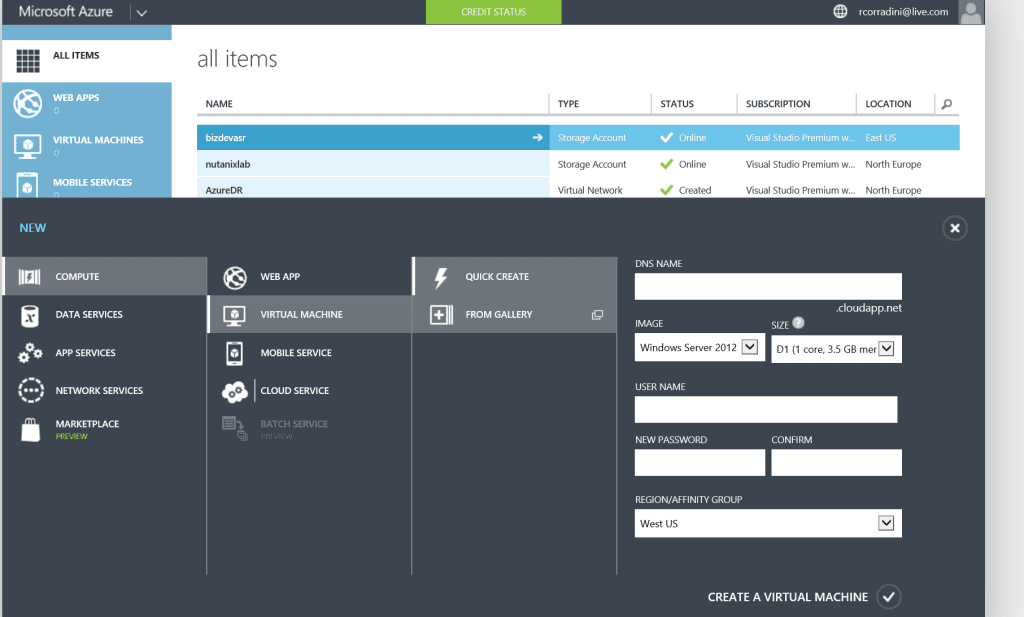
The other option, called From Gallery, lets you create a virtual machine by specifying advanced options presented in a series of pages. The first page shown below allows you to choose an image to be used as a template when creating your virtual machine…
Windows Azure Pack vs. Windows Azure
Let’s again review the definition that Microsoft uses for describing Windows Azure:
Windows Azure is an open and flexible cloud platform that enables you to quickly build, deploy, and manage applications across a global network of Microsoft-managed datacenters. You can build applications using any language, tool, or framework. And you can integrate your public cloud applications with your existing IT environment.
Now let’s examine how Microsoft describes Windows Azure Pack. First, here’s how they define Windows Azure Pack on their Server and Cloud Platform site:
The Windows Azure Pack is a collection of Windows Azure technologies available to Microsoft customers at no additional cost. Once installed in your datacenter, the Windows Azure Pack integrates with System Center and Windows Server to help provide a self-service portal for managing services such as websites, Virtual Machines, and Service Bus; a portal for administrators to manage resource clouds; scalable web hosting; and more.
Next, here’s how Microsoft defines Windows Azure Pack in the TechNet Library:
Windows Azure Pack for Windows Server is a collection of Windows Azure technologies, available to Microsoft customers at no additional cost for installation into your data center. It runs on top of Windows Server 2012 R2 and System Center 2012 R2 and, through the use of the Windows Azure technologies, enables you to offer a rich, self-service, multi-tenant cloud, consistent with the public Windows Azure experience.
Comparing these various definitions and reading the linked resources enables us to conclude the following about how Windows Azure Pack compares to Windows Azure:
- Both platforms provide a set of cloud services that allow you to build and deploy cloud-based applications using almost any programming language, framework, or tool. But while Windows Azure provides a broad range of several dozen different cloud services, Windows Azure Pack provides only a subset of these services, primarily Web Sites, Virtual Machines and Service Bus.
- Cloud applications running on either platform can easily be integrated with on-premises IT environments that utilize Windows Server to enable you to build hybrid solutions.
- While Windows Azure is hosted in globally distributed datacenters managed by Microsoft, Windows Azure Pack is something you can deploy within your own datacenter.
- And lastly the upcoming Azure Stack will be in full parity with Windows Azure…See my Azure Stack Article
To summarize, Windows Azure Pack lets you bring some of the capabilities of the Windows Azure public cloud platform right into your own datacenter by leveraging your existing infrastructure based on Windows Server and System Center.
In the next article of this series we’ll examine different deploying scenarios with Nutanix for Windows Azure Pack in your datacenter.
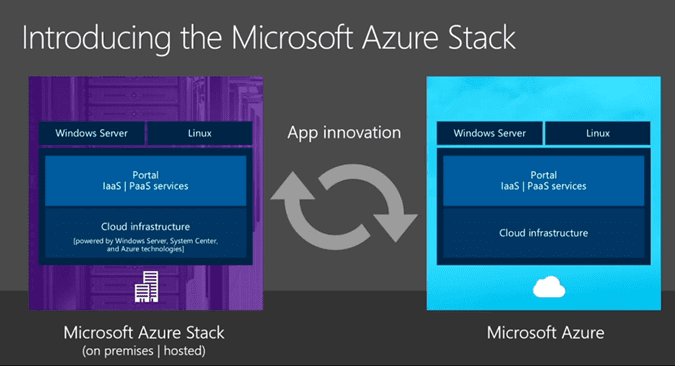
Azure Stack…What is it?
The Ignite 2015 conference in Chicago is where Microsoft made the official announcement of Azure Stack, its private cloud infrastructure for data centers that want to be Azure in their own right. Or in other words, on-premises will be in full parity with Azure Cloud.
Quotes from Brad Anderson from Keynote on Azure Stack
“If you think about Azure, there’s all the infrastructure that you’re aware of, in network, storage and compute. There’s a set of services like IaaS and PaaS that we deliver. And then there’s all your applications, and that, really, is what Azure is,” explained Brad Anderson, Microsoft’s corporate vice president for cloud and enterprise, during a keynote session Monday morning. “Two years ago, we announced we were going to bring portions of this to your data center, and we called it the Azure Pack.”
Portions of this Azure Pack had made their way onto partner vendors’ hardware in the past — in the form of Microsoft Private Cloud Fast Track Program and Dell’s Cloud Platform System. My company, Nutanix was one of the first Private Cloud Fast Track Partners with certified reference architecture. So we’ve seen private cloud platforms with third-party vendor brands, built around server software made by Microsoft but not called Windows.
What Azure Stack becomes, over and above Azure Pack, is not just a microcosm of Azure, but an extension of Azure itself. As several Microsoft officials confirmed at Ignite, Azure Stack extends the file and object system of Azure into the private space. (And Azure Stack won’t be the only Microsoft technology that does this….Hint, Hint…Hmm…under NDA at moment)
“You want to be able to take those cloud applications, and host them in your environment,” said Anderson. “You’ve told us you want Azure — all of Azure — in your data centers. Azure Stack … is literally us giving you all of Azure to run in your data centers.
I saw early demonstrations of Azure Stack at Ignite, and what I saw was user access policy management system that essentially duplicated the one currently used on the public Azure cloud as shown below.
“The Microsoft Azure Stack gives application owners the ability to ‘write once, deploy anywhere,’ whether it be to your private cloud, a service provider’s cloud, or the public Azure cloud,” reads a post to Microsoft’s server and cloud blog Monday. “Developers will have the broadest access to application development platforms across Windows and Linux to build, deploy and operate cloud applications using consistent tools, processes and artifacts. One Azure ecosystem across public, private and hosted clouds will allow you to participate in a unified, robust partner network for Azure clouds.”
Microsoft’s idea is to make private cloud space and public space addressable and manageable using the same tool set, and by extension, to effectively make data centers into planks, if you will, for Azure. It’s one big reason why the words “Windows Server” are being spoken less and less often by people whom you would think were in charge of it.
Azure Stack Deeper Dive
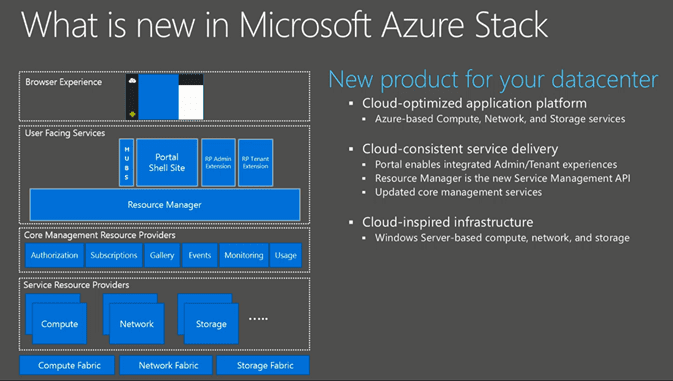
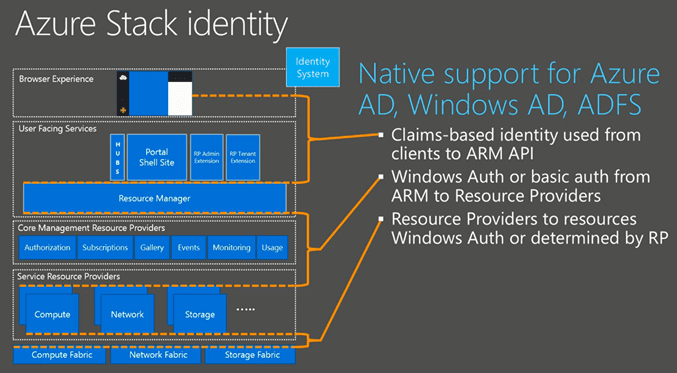
Now let’s start at the top. When we look at the image below we see the browser experience. In the current version of Azure Pack we have 2 portals, 1 for the tenant and 1 for the admin. In Azure Stack we have 1 browser experience. That experience is also the same across Azure Stack and Azure. So admins as well as the tenants go through the same portal site and leveraging the same portal API’s and extensions.
In the deployment of the portal site there is still an option to scale out to multiple website nodes like we do with a distributed deployment of Windows Azure Pack today. When we go down that rabbit hole, we see the Azure Resource Manager and the Core Management Resource Providers. The Core Management Resource Providers integrate in Azure Resource Manager and all components interact with that. Below in this post, I will focus on the Azure Resource Manager and the Core Resource Providers. Further down we see the Service Resource Providers. The Service Resource Providers will control and manage the resources it is assigned to. Like the Compute Service Resource Provider will manage the compute resources (nodes), the Storage Resource Provider will manage the storage resources (nodes) and so on…
And that’s really in a nutshell the top to bottom service layout of the Azure Stack.
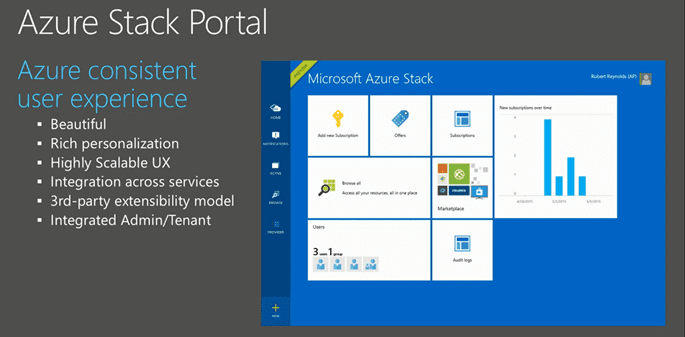
Let’s look at the portal. The portal is completely redesigned and which allow you to fully personalize. It is highly scalable and have integration across services. When you install new resource providers today in WAP you need to edit the core code for the Azure Pack portal. Then you need to restart the web service process to see the result of that change. With the new design the portal process runs continuously in a separate process and when you extend the portal by adding extensions a workflow will distribute the extensions to all nodes running the portal site. As mentioned before the admin and tenant site are integrated in the same portal.
The portal UI is very nice, but it would be useless if we cannot login to the portal, right? Let me talk about the identity part of the new Azure Stack. In the old portal we had the options to use the SQL .Net membership or we could integrate ADFS to use AD or other federated identity providers (IDP’s). In the new portal they use claims-based authentication and there is native support for the following:
- Azure Active Directory
- Windows AD
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
From the Azure Resource Manager to the Core Management Resource Providers it will use Windows Authentication or Basic Authentication. The Core Management Resource Providers will use Windows Authentication or an authentication method defined by the Resource Provider.
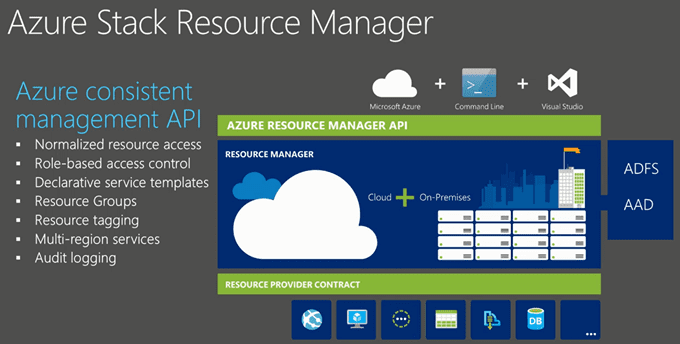
Now on to the Azure Resource Manager. The Azure Resource Manager is the new Service Management API. It’s as Microsoft calls it “a product” that allows the management of the compute, storage, network. When you, as a tenant, create a resource group it allows you to put all the resources (VM’s, Networks, websites etc…) in a resource group that can be managed as a whole (Create /Add / Update /Delete – aka Life Cycle Management).
With role based access control (RBAC) you, as a tenant, can also provide access to other users that have access based on the permission you assign to the resource group. Also usage is collected for a particular resource group so you can see how much the resources in a resource group will cost.
The Azure Resource Manager will also allow you to put deployments in regions. Regions represents the datacenters of your service provider or your own datacenters. Furthermore the Azure Resource Manager is providing audit logging on your subscriptions and resources. To create resources using the Azure Resource Manager you need to create or use an existing template. A template is a json file what can be edited to define the resources in your deployment.
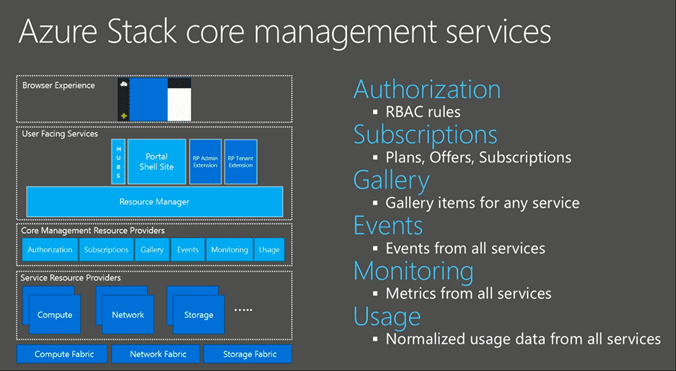
The Azure Resource Manager will talk to the Core Management services. Let’s look at the components involved in that.
- The Authorization Service: By using RBAC, it allows us to granular assign permissions to resource groups. Subscriptions are assigned to tenants that have a plan defined.
- The Subscription Management Service is responsible for managing the Service Plans, Offers and subscriptions. You can even use Azure Resource Manager templates to define new subscriptions based on a template you have defined.
- The Gallery Service is a core common service that will work across any of the connected services. Admins as well as tenants are allowed to put their own gallery items in it.
- The Events Service is a collector to collect all events across all the services
- The Monitoring Service collects metrics from all services.
- And last but not least we have the Usage Service which will collect the usage per service for each tenant / resource group.
So this what I know so far from MS, but will update this post as I know more. MS is not giving defiant answer, but rumors are beta late fall and Tech Preview in spring. I can’t wait to get the early bird bits to play around with it and when I do I will follow-up on this post to give you more technical information of Azure Stack!
Until next time, Rob…

 Admin Portal
Admin Portal User Signin Portal
User Signin Portal User Main Portal
User Main Portal